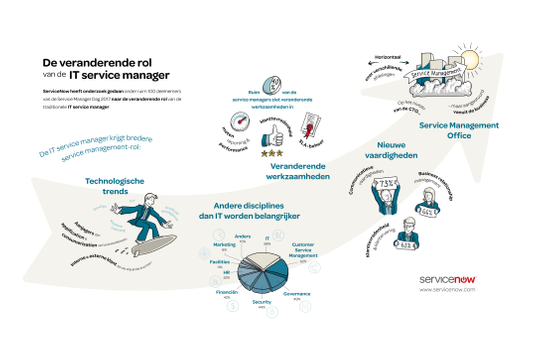
Although IT is mentioned as an important part of the service management function by 88%, other disciplines are also becoming more and more important. In this case, 62% of respondents mentioned customer service management, 48% of governance, and 43% of security. Human resources, facilities and marketing seem to lag behind. However, it is surprising that among the respondents with business background, human resources are indeed an important part of the service management function.
Sebastiaan Laurijsse, senior director of IT infrastructure services at NXP, recognized the research results of the chip manufacturer’s daily practice. The need for faster delivery and adoption of new applications by internal business units has led to changes in the structure of NXP’s internal service management processes. The result is that IT is now actually a business enabler. Therefore, there are much more “new” service managers than previous full-service providers, and they must operate both at the strategic and operational levels. “
“App” promotes role change
Research shows that the consumerization of business services and “applications” (service automation and standardization are the core) are the main driving forces (37%) of the change in the role of service managers. Companies must be able to provide employees and customers with a service experience that has been accustomed to consumers for years. Also mentioned artificial intelligence, and the rise of cloud services and DevOps. Only 14% of respondents said that the change in the role of service managers has nothing to do with technological development.
Research shows that service management will play a broader role within the organization. Paul Hardy, Chief Strategy Office of ServiceNow Europe, Middle East and Africa, said that where service management was originally built vertically, we are now increasingly seeing horizontal applications across departments. “We think it’s time to establish a so-called service management office. This operation is at the same level as the CTO but managed by the enterprise. The new interpretation of the service management role requires different professional skills, less IT thinking and more Business thinking.”
Reduce IT, increase business
More than 40% of IT service managers said that their activities have changed in the past year. When asked about the areas where this change occurred, it mentioned measurement, reporting and performance (60%), ensuring customer satisfaction (53%) and SLA management (51%). 60% of IT service managers believe that their role is currently mainly tactical. One-third of people believe that performing their duties is essentially tactical and strategic.
Marjon Diepeveen, service manager of ABN AMRO, has experienced the changing role of traditional IT service managers in practice. “Five years ago, this position was mainly for operations. Especially in the past year, I have seen this role become more and more strategic. In the development of products and services, the importance of the enterprise has been increasingly influenced by people Pre-requirements. Thanks to the agile way of working, you are also better able to continuously monitor usage and business benefits in the life cycle of products and services.”
Customer causes change
According to survey respondents, internal and external customers are the driving force behind the changing role of service managers. They also indicate that service managers must have different skills and capabilities from traditional IT service managers. With these new skills, “softness” becomes more and more important: the most frequently mentioned are communication skills (73%), business relationship management (66%), and ensuring customer satisfaction and customer experience (63%).
About the research
This article is a submitted message and is not the responsibility of the editor.
#ServiceNow #portrays #changing #role #service #managers
More from Source